October 14, 2011
Current Status of Wind Power in Japan (2010)
Keywords: Renewable Energy
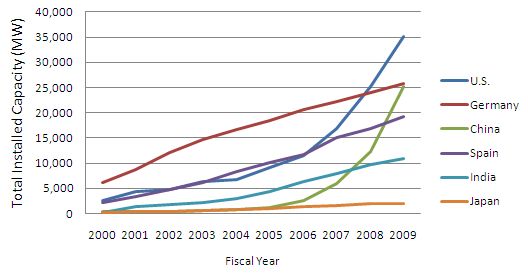
Total Installed Wind Capacity, by Country
While new wind power installations are skyrocketing globally, in recent years Japan has seen a stagnation of growth in its annual installed wind capacity. Reasons for this trend include limitations on the capacity that can be recruited in areas that already have many installations, because of restrictions on grid capacity. This leads to lotteries and bidding over installation rights. In addition, at a time when there are various location restrictions, the slump in electricity prices caused by the RPS law and the lack of transparency toward future laws also play a role. Moreover, the business profitability of wind power installations is worsening as installation costs increase, caused by the global increase in demand for wind power facilities and facility specifications unique to Japan.
Installed wind power capacity and policies promoting installations, by country, are as follows:
and Policies Affecting Wind Power Generation, by Country
| Country | New Capacity 2009 (MW) | Total Installed Capacity (MW) | Policies, etc. | |
| 1 | China | 13,000 | 25,104 | Feed-in Tariff (total capacity) |
| 2 | U.S. | 9,922 | 35,159 | State policies (mostly RPS), and Federal Government's Production Tax Credit (PTC) |
| 3 | Spain | 2,459 | 19,149 | Feed-in Tariff (total capacity) |
| 4 | Germany | 1,917 | 25,777 | Feed-in Tariff (total capacity) |
| 5 | India | 1,271 | 10,926 | |
| Japan | 178 | 2,056 | Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) Law |
References:
- REN21: Renewables 2010 Global Status Report
- GWEC Global Wind 2008 Report
- GWEC Global installed wind power capacity 2008/2009
Back to Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
- 'Yumekaze' Wind Turbine Project Connects Metro Consumers and Regional Producers: Seikatsu Club Consumers' Co-operative
- Shaping Japan's Energy toward 2050 Participating in the Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Nishiawakura's Initiative for 100% Energy Self-Sufficiency, and a Municipal ICO Scheme
- Actions Toward 100% Renewable Energy in Japan
- Sustainable Community Building in Shimokawa: Recycling-Oriented Forest Management Enabling Permanent Use of Forest Resources
Related
"Popular Articles"
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2015)
- Offshore Wind Farm Withstands Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2014)
- Geothermal Power: Japan Has World's Third Largest Geothermal Reserves, 60 Percent of Which Can Be Developed
- Tokyo Plans to Increase Renewable Energy Ratio to 20% by 2024


