Energy / Climate Change
December 8, 2003
Maple Leaves Turn Red 2 Weeks Later Than They Did 50 Years Ago
Keywords: Climate Change Ecosystems / Biodiversity Government University / Research institute
Copyright The Japan Meteorological Agency
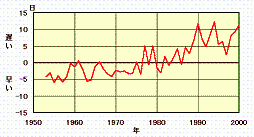
The arrival of autumn at each site is determined by the date on which roughly 80 percent of leaves of sample maple trees have turned red. The attached line graph shows year-to-year variations on the arrival of the autumn maple leaf season in Japan. The figures in the graph were calculated using data collected from 44 sites from which adequate data were available, and show the average differences between the autumn arrival date for each year and the average year, using data for the 30 years between 1971 and 2000.
Until the mid 1970s, most points on the graph are below zero, meaning that maple leaves tended to turn red earlier than average. In contrast, after the late 1970s, with few exceptions, the advent of autumn leaf season became later than the average year, and since the late 1980s the season has come almost five to ten days later than the average year.
Meanwhile, Japan's annual average temperature has risen by approximately one degree Celsius during the 100 years between 1901 and 2000. In Metropolitan Tokyo, the average temperature for the 1960s was 0.5 degrees C below temperatures for an average year, 0.3 degrees C below average for the 1970s, and 0.1 degrees C below for the 1980s, but 0.5 degrees C above the average for the 1990s, showing a remarkable rise in that decade. Because the arrival date of the autumn leaf season is determined by temperatures in the early autumn of the same year, the delay in the autumn leaf season can be attributed partly to global warming.
Posted: 2003/12/08 10:35:32 PM
Japanese version
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
- Shaping Japan's Energy toward 2050 Participating in the Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Implementation of the Paris Climate Agreement: A Report on Japan's Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Auto Sales Industry Cooperates to Tackle Social Responsibility: Examples from Yamagata, Japan
- Yokohama FC: Leader in Eco-Activities through Football-Related Carbon Offset
Related
"Popular Articles"
- Large Ozone Hole Observed Again in 2011
- Japan's Pro Baseball Teams Start Eco-Project to Cut Energy Use by 6%
- Manufacturer Saving Energy by Growing Vertical Gardens on Factory Walls
- Sony Draws Up 'Road to Zero' Plan for Zero Environmental Footprint
- Tokyo Announces Innovative 10-Year Strategy against Climate Change


