ProjectsPast and current JFS projects
What is Sustainability?
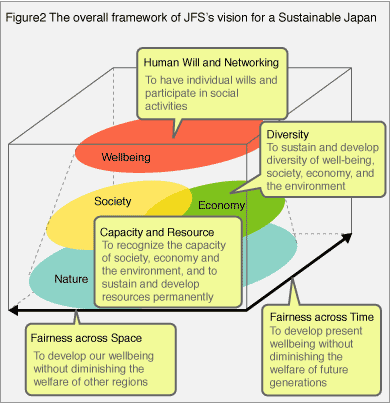
Five value compositions
JFS considers “Sustainability” as from five basic compositions. We have studied several definition of sustainability in the world including the definition of “Sustainable Development” made by the Brundtland Commission. After a comparative review of them, JFS defined the five basic compositions from our own point of view.
- Capacity and Resource
To live socially and economically satisfactory lives within limited global natural resources and carrying capacity, and consider a mind of appreciation and “MOTTAINAI (Waste Not, Want Not)” - Fairness across Time
To receive the inheritance of previous generation and pass it on to future generation correctly. - Fairness across Space
To distribute wealth, goods and resources between nations and regions in an equitable way, and there is no exploitation from one to another - Diversity
To respect the diversity of individuals, species, culture, which is also of other organisms - Human Will and Networking
Individual's will to build a better society, networking through communication with others, flexible and open mutual dialogues and social participation
JFS defines Sustainability as follows:
“Acts by humankind that respect the diversity of all creatures, and result in the passing on of life, nature, livelihoods and culture to future generations within the carrying capacity of the natural environment, and the establishment of mutual connections with the purpose of building better societies and seeking the greatest happiness of the greatest number across both time and space.
Four Areas
To capture the context of “Sustainability” more comprehensively, JFS adopted the followings four areas, which is from a framework of “Sustainability Compass” developed by Mr. Alan AtKisson, an environmental consultant based in Sweden, with referring to the concept of “Triple bottom line” advocated by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and others.
- Nature
Natural, global and local environments including the concepts of resource capacity and biodiversity. A fundamental concept of sustainability. - Economy
Something which enriches human life and makes the life easier by providing goods and services. An economic activity in general - Society
Social activity, government, school, community, etc. An aggregation of human life. - Wellbeing
Individual's self-actualization, pursuit of happiness, social participation, and improvement of quality-of-life.
Overall Framework of JFS’s vision for a Sustainable Japan